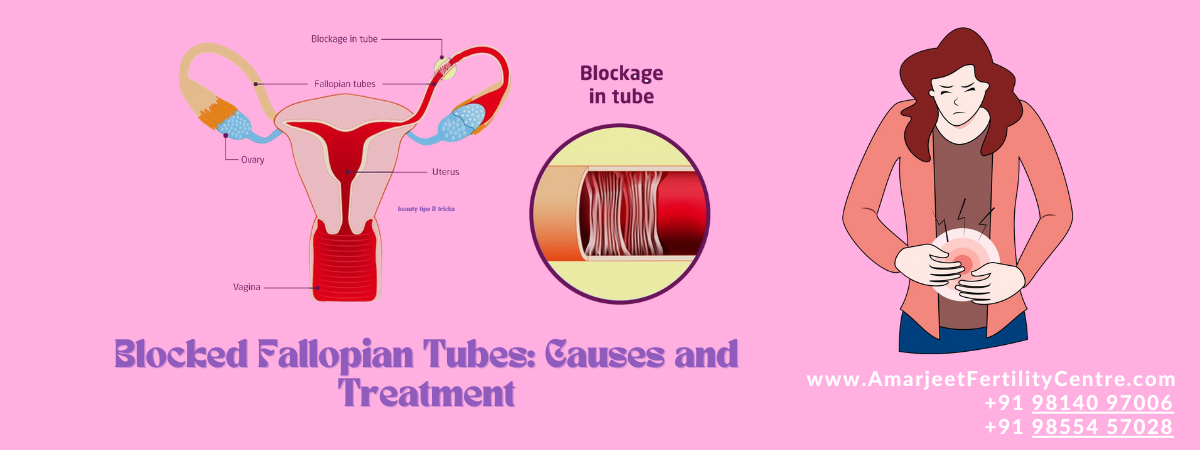
Blocked fallopian tubes, also known as tubal occlusion, are a significant cause of female infertility. The fallopian tubes play a crucial role in reproduction, serving as the pathway for the egg to travel from the ovaries to the uterus and where fertilization by sperm typically occurs. When these tubes are blocked, the sperm cannot reach the egg, or the fertilized egg cannot reach the uterus, leading to infertility. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for blocked fallopian tubes is essential for women facing this condition.
Causes of Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Several factors can lead to the blockage of fallopian tubes, including:
- Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID): PID is a common cause of blocked fallopian tubes. It is an infection of the female reproductive organs, often caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia or gonorrhea. The infection can cause scarring and damage to the fallopian tubes, leading to blockage.
- Endometriosis: This condition occurs when the tissue that normally lines the inside of the uterus grows outside of it, including on the fallopian tubes. Endometrial tissue can cause blockages by creating adhesions or scar tissue.
- Previous Abdominal or Pelvic Surgery: Surgeries, particularly those involving the fallopian tubes, ovaries, or uterus, can lead to the formation of adhesions. These adhesions can block the fallopian tubes.
- Ectopic Pregnancy: An ectopic pregnancy, where a fertilized egg implants and grows outside the main cavity of the uterus, can cause damage and scarring to the fallopian tubes, leading to blockage.
- Hydrosalpinx: This is a condition where the fallopian tube is blocked and filled with a watery fluid. The blockage can be caused by an infection, previous surgery, or endometriosis.
- Congenital Tubal Blockage: In rare cases, a woman may be born with blocked fallopian tubes due to a congenital condition.
Symptoms of Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Blocked fallopian tubes often do not present any specific symptoms. Many women are unaware they have the condition until they experience difficulties in conceiving. However, some symptoms can be associated with the underlying causes of tubal blockage, such as:
- Pelvic Pain: Chronic or intermittent pain in the pelvic region, often associated with endometriosis or PID.
- Painful Periods: Severe menstrual cramps or pain during menstruation.
- Unusual Vaginal Discharge: Abnormal discharge can be a sign of an infection like PID.
- Pain During Intercourse: Discomfort or pain during sexual activity.
Diagnosis of Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Diagnosing blocked fallopian tubes involves a series of tests and procedures:
- Hysterosalpingography (HSG): HSG is a specialized X-ray procedure used to check for blockages in the fallopian tubes. A contrast dye is injected into the uterus through the cervix, and X-ray images are taken to observe the flow of the dye through the fallopian tubes.
- Sonohysterography: This ultrasound-based test involves injecting saline into the uterus to get a clearer image of the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes.
- Laparoscopy: A minimally invasive surgical procedure where a thin, lighted tube (laparoscope) is inserted through a small incision in the abdomen to directly view the fallopian tubes and other pelvic organs. It allows the doctor to see any blockages, adhesions, or other abnormalities.
- Blood Tests: Blood tests can be conducted to check for infections or conditions like endometriosis, which may cause tubal blockages.
Treatment Options for Blocked Fallopian Tubes
The treatment for blocked fallopian tubes depends on the severity and cause of the blockage, the woman’s age, overall health, and her desire to conceive. Treatment options include:
Medical Treatments
- Antibiotics: If the blockage is caused by an infection like PID, antibiotics can treat the infection. However, they cannot repair any damage already done to the fallopian tubes.
Surgical Treatments
- Laparoscopic Surgery: This minimally invasive surgery can remove blockages, adhesions, or scar tissue from the fallopian tubes. In cases of hydrosalpinx, the affected portion of the tube can be removed, or the entire tube may be removed if necessary.
- Tubal Reanastomosis: This microsurgical procedure reconnects the parts of the fallopian tube after a blockage has been removed. It is often used for women who have had tubal ligation (a surgical sterilization procedure) and wish to reverse it to conceive.
Assisted Reproductive Technologies (ART)
- In Vitro Fertilization (IVF): IVF is a widely used fertility treatment for women with blocked fallopian tubes. The process involves retrieving eggs from the ovaries, fertilizing them with sperm in a laboratory, and then transferring the resulting embryos directly into the uterus, bypassing the fallopian tubes.
- Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI): ICSI is often used in conjunction with IVF. A single sperm is injected directly into an egg to assist fertilization, which is particularly useful if there are also male infertility issues.
Natural and Alternative Treatments
While medical and surgical treatments are typically required to treat blocked fallopian tubes, some women explore natural and alternative therapies to improve their fertility. These methods are not scientifically proven to unblock fallopian tubes but may support overall reproductive health:
- Herbal Remedies: Some herbal supplements are believed to support reproductive health and reduce inflammation, although their effectiveness is not scientifically established.
- Acupuncture: Acupuncture is thought to improve blood flow and reduce stress, potentially supporting fertility.
- Diet and Lifestyle Changes: Maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, and managing stress may improve overall reproductive health.
Conclusion
Blocked fallopian tubes are a common cause of female infertility, often resulting from conditions like PID, endometriosis, or previous surgeries. Symptoms may be subtle or absent, making diagnosis challenging without medical testing. Various diagnostic tools, including HSG and laparoscopy, help identify the presence and cause of blockages. Treatment options range from antibiotics and surgical interventions to assisted reproductive technologies like IVF. While natural remedies may support reproductive health, they are not substitutes for medical treatments. Women experiencing infertility should consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate course of action based on their individual circumstances. With the right treatment and support, many women with blocked fallopian tubes can achieve their dream of becoming mothers.